A research team led by Professor Chulhong Kim (EE, CiTE, ME, GSCST) and Prof. Yong Joo Ahn (CiTE, GSCAT) has made a breakthrough in stroke treatment, with an advanced technology that combines light and sound. The findings have been published in Advanced Science, an international academic science journal.

Ischemic strokes occur due to the blockage of blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. It is difficult to recover from it unless treated promptly, as the damage to brain tissue accelerates over time. Formerly existing technologies, such as CT or MRI scans, had limitations in monitoring changes in blood vessels in real-time during the earlier stages, and research on animal models had setbacks in observation scope and efficiency.

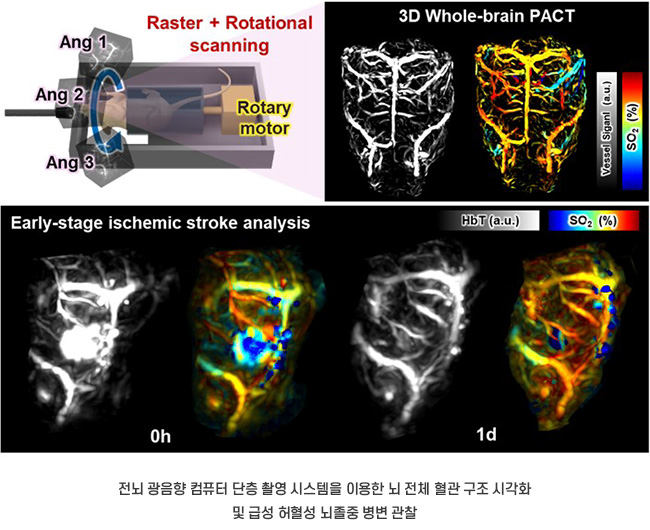
In order to address this issue, the research team has developed photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT) technology that combines light and ultrasound. The team obtained a brain image by compounding images from various angles, using a complex scanning method that combines rotational and raster scanning. This technique is similar to reconstructing a 3D image from pictures taken from various directions. By using this technology, the team successfully monitored changes in the cerebrovasculature of small animals at the early stage of ischemic stroke, in real-time and non-invasively. They also succeeded in precisely analyzing changes in blood vessels across a broad area.
Furthermore, the research team has observed hemoglobins non-invasively by utilizing multi-wavelength photoacoustic imaging in the near-infrared region (NIR). They also developed an algorithm to measure oxygen saturation for each blood vessel in real-time, which enables precise monitoring of collateral circulation of blood and changes in neovasculature, as well as ischemic stroke lesions. This is the result of testing the reliability of the new system compared to previous pathology examinations, which showed that the newly developed PACT system effectively tracks vascular recovery after stroke.
The research team explains, “The greatest accomplishment of this research is that it enables a precise observation of changes in blood flow without a contrast agent.” They added, “This will provide a new experimental approach for research, not only in the treatment of stroke but also in neural and vascular diseases.”
This research was supported by the BK21 FOUR program of the National Research Foundation (NRF), ICAN program, the Korea Medical Device Industry Association (KMDIA), the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), Global University 30, and the Hyundai Motor Chung Mong-Koo Foundation.


